

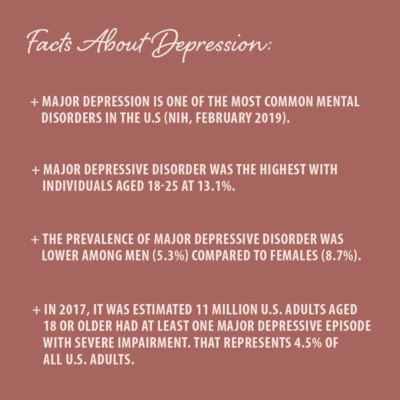
It’s not uncommon for someone that has depression to also suffer from anxiety or vice versa. Approximately half of the population diagnosed with depression are also diagnosed with an anxiety disorder.
Anxiety Disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) = persistent and excessive worry about several different things (money, work, relationships, health, other issues).
-
- Difficulties in controlling their worry
- Worrying more than seems warranted
- Expect the worst
- Anticipate disaster
- Typically accompanies Major Depression Disorder (MDD)
Panic Disorder (PD) = experience spontaneous seemingly out-of-the-blue panic attacks and are very preoccupied with the fear of a recurring attack.
-
- Panic attacks occur unexpectedly
- Can awaken from sleep in a panic
- Cause those to miss work, school
- Avoid situations that fear them to have panic attack
- Attend many doctors’ visits
Social Anxiety Disorder = intense anxiety or fear of being judged, negatively evaluated, or rejected in a social or performance situation.
-
- Symptoms: rapid heart rate, nausea, sweating
- Worry about appearing anxious (blushing, stumbling over words)
- Avoid social or performance situations
- Often feel powerless against their anxiety
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) = experiencing obsessions (unwanted thoughts, images or urge) and compulsions (feel compelled to perform) that causes distress and anxiety.
-
- Common Obsessions: contamination, cleanliness, aggressive impulses or need for symmetry
- Common Compulsions: checking, washing/cleaning, arranging
- Not a clear logical connection between obsessions and compulsions
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder = serious and potentially debilitating condition that can occur in people who have experienced or witnessed a natural disaster, serious accident, terrorist incident, sudden death of a loved one, war, violent personal assault such as rape, or other life-threatening events.
-
- Often occurs with depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse
- Troubles with their close family relationships or friendships
- Symptoms: issues with trust, closeness, communication, problem-solving
Depression Disorders
Major Depression Disorder (MDD) = Overwhelming feeling of sadness or a loss of interest and pleasure in most usual activities.
-
- Symptoms lasting 2 weeks or longer: increase or decrease in appetite, insomnia or sleeping too much, constant fatigue, feelings of worthlessness, guilt, plans for suicide, brain fog, diminished abilities to think clearly, concentrate or make decisions.
- Key: symptoms start affecting social, occupational, educational or other aspects of life and are impacting activities of daily living or quality of life.
Persistent Depressive Disorder or Dysthymia (lack of pleasure or interest in doing things that you used to) = Mood disorder feeling low, dark or sad mood that is persistent and present for most of the day and on most days, for at least 2 years.
-
- Symptoms: irritability, poor appetite or overeating, insomnia or sleeping too much, low energy, low self-esteem, poor concentration.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) = Severe and sometimes disabling extension of premenstrual syndrome with sadness, hopelessness, tension, extreme moodiness, irritability or anger.
-
- Mood changes are more severe than with PMS. Disruption in social and work life that typically begins 7-10 days before the menstrual period and continues for the first few days of the cycle.
- Symptoms: breast tenderness, bloating, fatigue, sleep pattern changes, eating habit changes
Adjustment Disorder = depression that is triggered and then diagnosed within 3 months of a stressor that involves a change in life (new job, marriage, divorce, baby, death, illness).
-
- Symptoms typically resolve in 6 months when the individual begins to cope and adapt to the stressor or the stressor is removed.
- Treatment is typically time-limited and relatively simple. Additional support during that stressful time will help the person to adapt and recover.
Seasonal Affect Disorder (SAD) = depression is related to changes in the length of days or the season.
-
- Typically, those suffering from SAD have Major Depression Disorder during this specific time of year, typically winter when the days are shorter and there is a lack of sunlight.
Chronic Physical Illness’ can cause depression and anxiety, which can make the symptoms of the physical illness worsen and more difficult to treat.
-
- Eating disorders
- Headache/Migraine
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Sleep Disorders
- Substance Abuse
- Adult ADHD
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Stress
It is important to recognize these disorders, behaviors, and symptoms in yourself or others to get the help and treatment that is available to everybody of regardless of age. Treatment could be learning tools with mindfulness, meditation, counseling, and/or medication management.
Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death in the United States according to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP.org). It is important to know that you are not alone and there are many out there feeling the same way you are and there is HELP!
Sources:
-
- NIMH: Depression Basics. February 2019. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/major-depression.shtml
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA). 2018. https://adaa.org/about-adaa/press-room/facts-statistics
- American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. 2020. https://afsp.org/



